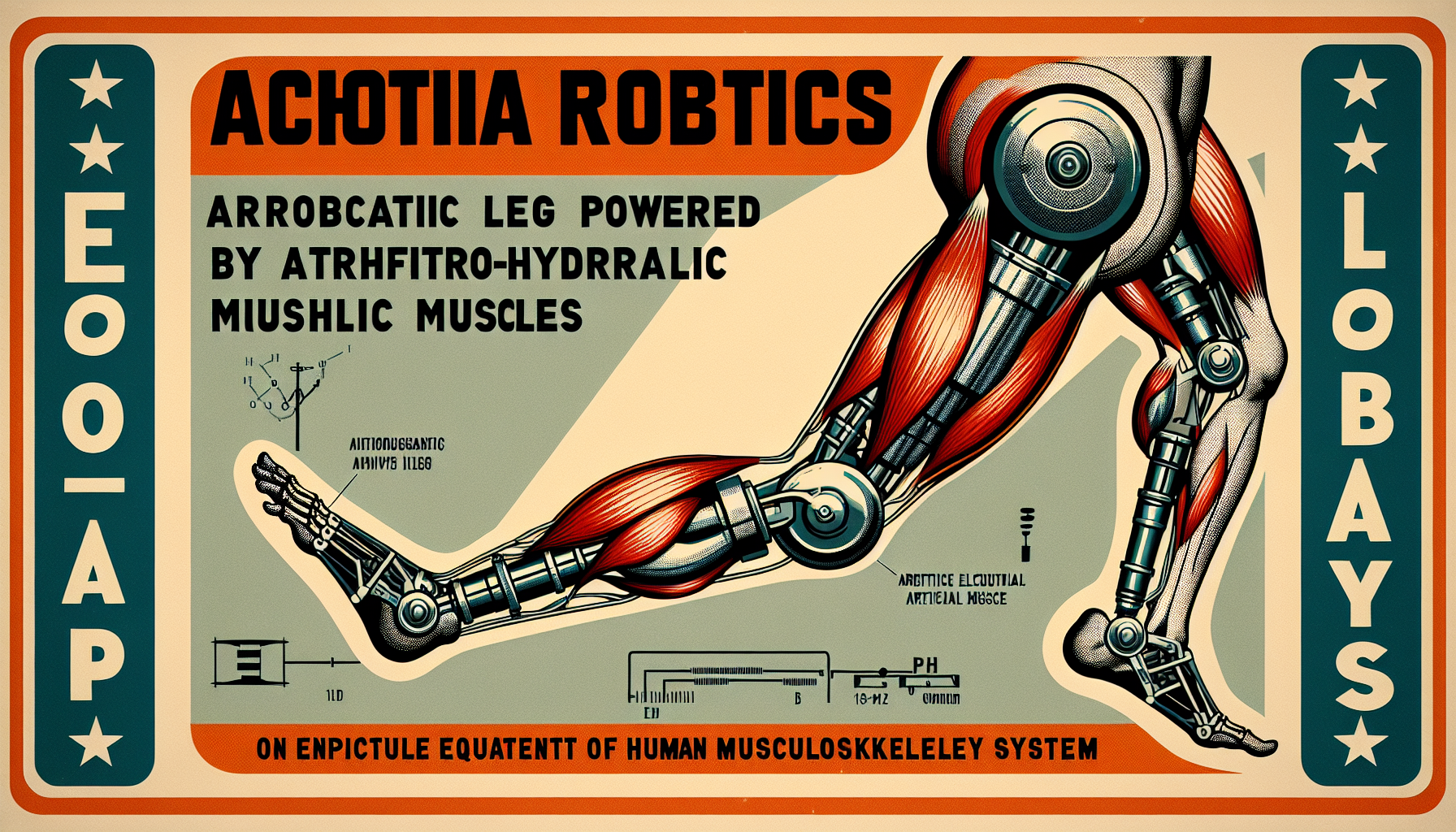
In the ever-advancing world of robotics, researchers at ETH Zurich and the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems have made a groundbreaking discovery. They’ve developed a robotic leg that uses artificial electro-hydraulic muscles, closely mimicking the human musculoskeletal system.
Energy Efficiency and Adaptability
This new robotic leg stands out for its amazing energy efficiency. Traditional robots often use rigid, energy-hungry parts that can limit how they move. But the artificial muscles in this robotic leg make it use less power while still being very mobile.
Another remarkable feature is how well it adapts to uneven surfaces. The human musculoskeletal system’s flexibility helps us move easily across varied terrains. By imitating this system, the robotic leg can handle different environments better, making it ideal for tasks like search and rescue, outdoor exploration, and industrial work.
Technological Innovations
The creation of these artificial muscles involves cutting-edge materials and control systems. Electro-hydraulic muscles are designed to contract and relax like human muscles, allowing the robotic leg to move naturally and efficiently. This not only enhances its physical abilities but also offers more precise control.
Implications for Robotics and AI
This breakthrough is part of a bigger movement in robotics and artificial intelligence (AI). Machines are being built to better emulate human capabilities. Combining AI with these robotic systems could lead to even smarter robots that can learn, adapt, and perform complex tasks on their own.
For example, when paired with agentic AI—a type of AI that makes decisions and takes actions without constant human supervision—these robots could become even more autonomous and effective. Recent developments in agentic AI show its ability to execute tasks, generate code, and interact with tools, making it a perfect match for advanced robotic hardware.
Future Applications
The possibilities for this technology are vast. In healthcare, robots with human-like muscles could help in rehabilitation, offering more natural and effective therapy. In industrial settings, these robots could take on tasks that require precision and flexibility, such as assembly and maintenance.
Moreover, this advancement could lead to more sophisticated humanoid robots that interact with and assist humans in daily tasks, boosting productivity and quality of life.
Conclusion
The creation of a robotic leg with artificial electro-hydraulic muscles is a major milestone in robotics. By mimicking the human musculoskeletal system, these robots achieve better energy efficiency and adaptability, making them suitable for a wide range of applications. With the continuous advancement of AI, integrating these technologies promises to revolutionize how robots can help us, opening up exciting new possibilities for the future.
Leave a Reply